It’s important that every nation in the world faces the task of eradicating global poverty. Although poverty exists in all nations, roughly 60% of the world’s poor (in 2019) lived in Sub-Saharan Africa alone, while 81% of the global poor at the poverty line of $3.65 lived in Sub-Saharan Africa or South Asia.

Source: Pexels
The causes of poverty in these regions are complex. They include economic policies that exclude the poor and are biased against them:
- A lack of access to markets and meaningful income-earning opportunities
- Inadequate public support for microenterprises (through initiatives like low-interest credit and skills training)
- A lack of infrastructure
- The widespread use of old technologies in agriculture
- Conflicts and social strife
- Political elites taking advantage of poor communities
Eradicating Global Poverty: A Definition
Eradicating global poverty refers to the ambitious and overarching goal of eliminating all forms and dimensions of global poverty. This goal goes beyond merely reducing poverty rates. It seeks to completely eradicate the conditions and situations that cause people to live in extreme poverty and deprivation. Considerable progress has been made in reducing poverty in the last two decades. However, more needs to be done to reduce the rate of extreme poverty further. This will reduce the number of those living in extreme poverty (Liu et al., 2020).
Recently, the COVID-19 global pandemic has significantly increased the number of those who have found themselves recently poor. The World Bank estimates that in 2020, between 88 million and 115 million people fell into extreme poverty as a result of the pandemic. In 2021, an additional 23 million to 35 million people will fall into poverty. This brings new people living in extreme poverty to between 110 million and 150 million. The World Bank also points out that even before the pandemic, development for many people in the world’s poorest countries was too slow to raise their incomes. This enhanced living standards, narrowing inequality. The eradication of poverty continues to be a top priority on the international development agenda.
Source: Thai PBS World
“New technologies hold the promise of the future, from climate action and better health to more democratic and inclusive societies… Let us use them wisely, for the benefit of all”
– Antonio Guterres, United Nations Secretary-General, 2021
Ways in Which Technology Is Eradicating Global Poverty
Modern technology plays a crucial role in addressing and eradicating global poverty. Here are five major ways in which technology is contributing to this effort:
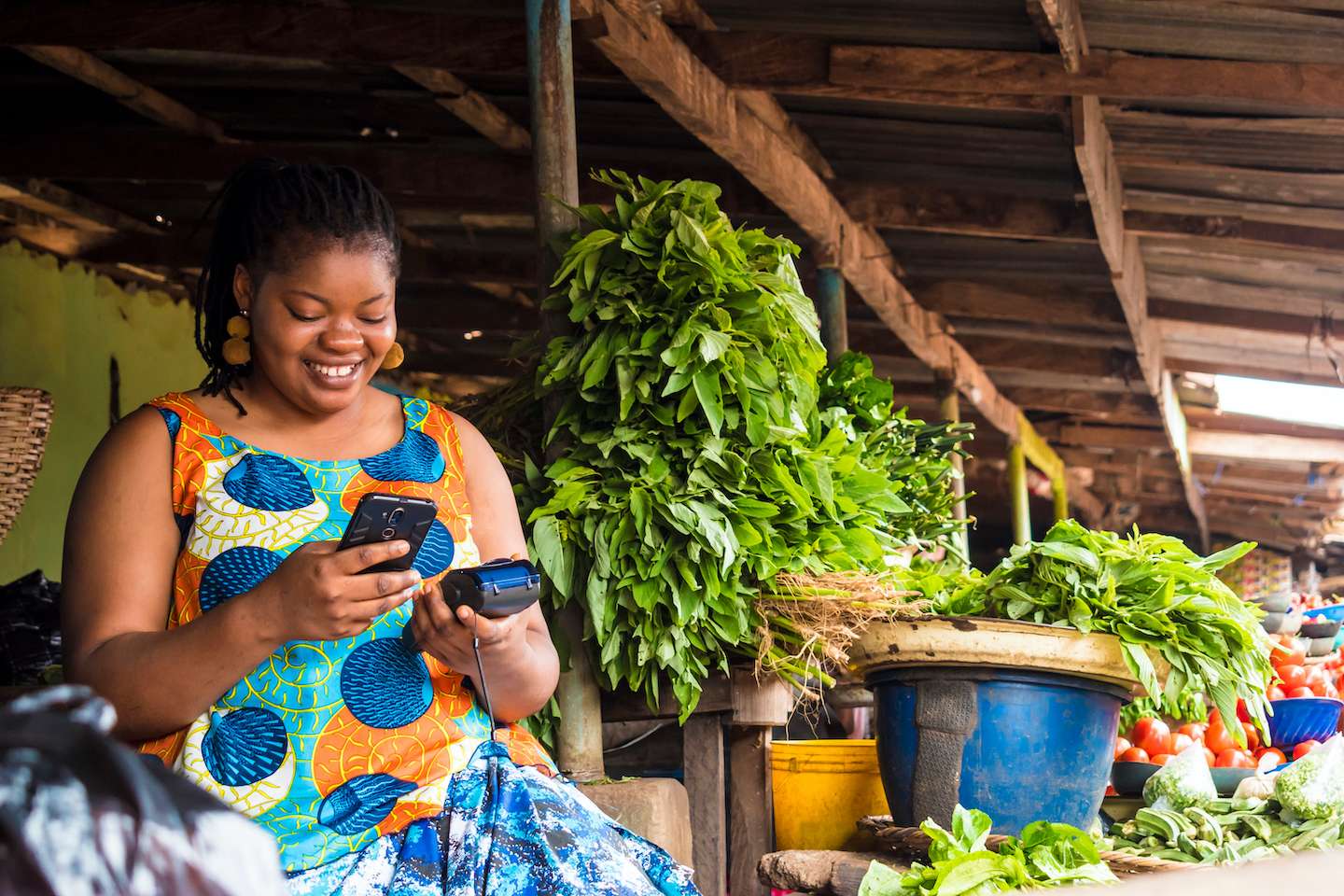
Financial and Mobile Technology Solutions
Financial technology (Fintech) is also known as internet finance. Fintech is inexplicably linked to mobile technology and is expected to continue to grow in unison. The introduction of mobile phones to rural Africa ranks highly among the factors credited with reducing poverty in the region. In villages distant from towns and cities, where most people do not have bank accounts or secure ways of storing their money, the biggest benefit of mobile use can be found.
Also, Fintech and mobile technology present new opportunities for women

Source: Econofact
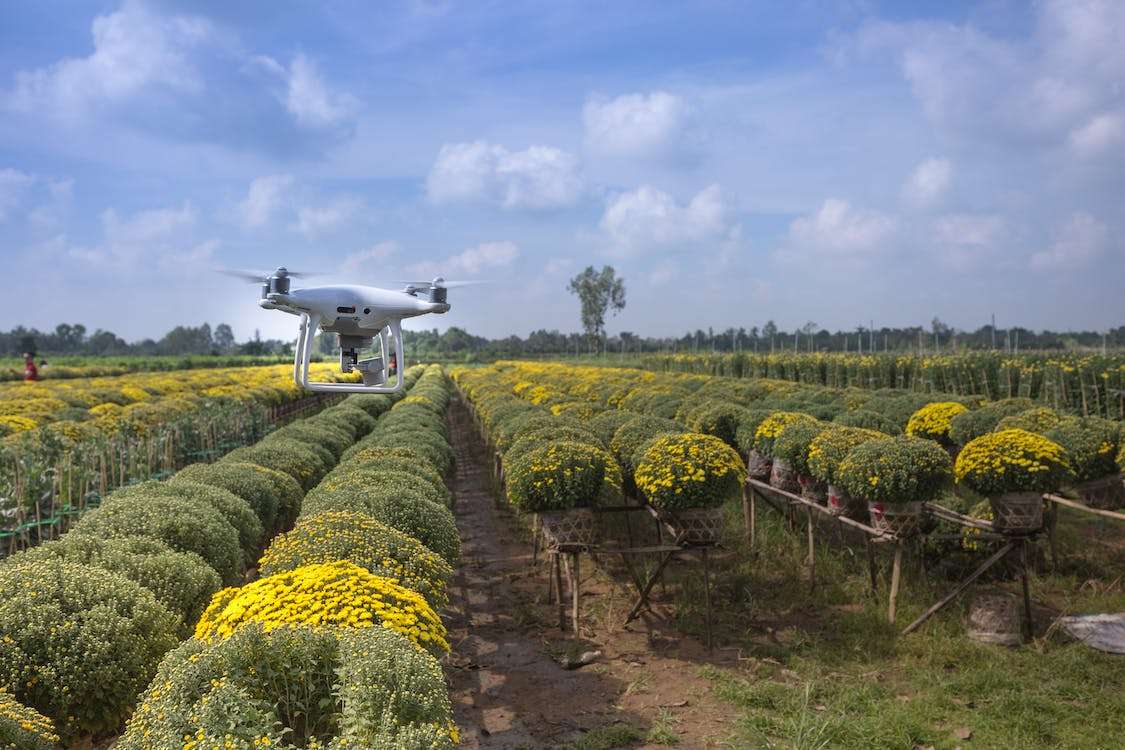
Agricultural Advancements
One of the possible solutions for fighting poverty is through improving productivity, profitability, and sustainability of smallholder farming (World Bank 2008). Most of the 1.4 billion people who live on less than $1.25 per day rely on agriculture for their livelihoods, according to the United Nations.
Increasing crop yields through technology involves various methods. For example, developing high-yielding crop varieties, improving irrigation techniques, and expanding the use of fertilisers and pesticides. It also encompasses precision agriculture, which employs technologies like GPS, sensors, drones, and data analytics to optimise farming practices. Additionally, satellite technology and remote sensing play a crucial role in monitoring crop health and land use patterns on a large scale.
Furthermore, scientists have developed Genetically Modified Crops (GMOs) to enhance crop resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental stressors. Biotechnological techniques, such as marker-assisted breeding and gene editing (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9), are utilised to create crops with improved traits. These include disease resistance, drought tolerance, and enhanced nutritional content. Likewise, smart farming systems and climate-smart agriculture are evident approaches due to advances in agriculture.
All are essential for achieving agricultural growth and development, as well as the subsequent reduction of poverty and its dimensions. This is because, apart from specific regions and situations, expanding traditional cultivation areas can no longer meet the rising demands of growing populations (Habtewold, 2021). The application of better agricultural practices stimulates economic development beyond agriculture and creates more employment opportunities for people elsewhere.

Source: Pexels
Clean Energy Sources
Access to energy enables people to work their way out of poverty, access education, and improve their own health. New technologies, such as solar and hydropower, can provide access to energy without building expensive power plants.
Solar technology has become more affordable and accessible, particularly in regions with unreliable electricity grids. Solar panels and home systems provide clean and reliable energy sources. This can further improve living conditions and enable economic activities for low-income households. Furthermore, improved cookstoves, often incorporating technology, reduce indoor air pollution and fuel consumption, benefiting both health and the environment.
Healthcare Improvements
Technological advances are helping to reduce poverty in a variety of ways. Another significant improvement is in healthcare. Such as improving healthcare access, lowering healthcare costs, preventing diseases, and enhancing the overall well-being of individuals and communities in developing nations.
For instance, In Kenya, the Mobile Alliance for Maternal Action (MAMA) provides expectant and new mothers with vital health information via text messages. This has improved maternal and child health outcomes by improving awareness and healthcare-seeking behaviour. Similarly, In Nigeria, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) uses digital tools and real-time data analysis to track disease outbreaks, respond to emergencies, and improve disease surveillance. This technology is crucial for managing epidemics and protecting public health. India has also introduced telemedicine initiatives like the Apollo TeleHealth Services and eSanjeevani. These connect patients in remote and underserved areas with healthcare professionals through video consultations and remote monitoring. This technology enables timely access to medical expertise and reduces the need for expensive travel.
Educational Improvements
Technological interventions enable people from underserved communities, including those in remote areas, to access quality educational resources and gain new skills. Through online learning platforms and open educational resources, the financial burden of education is reduced. Such technological resources include textbooks, videos, and interactive learning materials.

Source: Pexels
Challenges
Technology has immense potential to eradicate global poverty. However, it’s not a panacea, and it’s important to note that there are challenges to overcome. These challenges include:
- Digital Divide: The digital divide refers to the gap in internet access and technology literacy between different populations. Efforts must ensure that technology benefits reach marginalised and remote communities.
- Data Privacy and Security: As technology becomes more integrated into poverty reduction efforts, it’s crucial to address data privacy and security issues. This is to protect vulnerable populations from exploitation.
- Sustainability: Ensuring the sustainability of technology-based solutions is essential. This includes considerations such as maintenance, affordability, and long-term support for the infrastructure.
- Cultural and Contextual Sensitivity: Technology solutions must be culturally sensitive and adapted to the specific needs and contexts of the communities they serve to be effective and sustainable.
In all, technology has the potential to be a powerful tool in the fight against global poverty. However, addressing the challenges and considering cultural and contextual factors are crucial for these technological interventions to have a lasting impact on poverty reduction.
moving forward
Technology has a powerful influence on sustainable innovations. The effective implementation of technology has the ability to positively impact natural resources and enhance overall economic growth performance (Faltermeier and Abdulai 2008; Sanchez et al., 2009). When people rise meaningfully above poverty, many outcomes improve. This includes childhood mortality, life expectancy, years of schooling, and digital and financial inclusion. Life satisfaction increases significantly when people shed the stress of not being able to make ends meet. Eradicating poverty means more people can fulfil more of their material desires (Jebb et al., 2018).
Why is it essential that we focus on eradicating global poverty?
Undoubtedly, eradicating global poverty is a complex and long-term endeavour. It requires sustained commitment, resource allocation, and coordinated efforts on a global scale. International organisations, governments, and non-governmental organisations should work toward this goal through initiatives, policies, and programs. By aiming to improve the well-being of people living in poverty, we can address the systemic issues that perpetuate poverty.
The extent of multidimensional poverty is very high, and the impact of technology varies across regions and by sex, which requires concerted policy interventions (Habtewold, 2021). Fighting poverty also means guaranteeing other social benefits such as food security, increased rural income, etc. Policymakers should consider regional variations, community realities, and household characteristics. At the country level, this may require revising the national poverty reduction strategies to incorporate the multidimensional aspects of deprivation and consider appropriate technologies that most affect multidimensional welfare indicators, especially poverty, and its components.

Source: The LHoFT
Eradicating Poverty: The Goal
In addition, achieving the goal of reducing poverty and enhancing the living standards of the poor in developing nations is attainable with visionary leadership and political will committed to justice, equality, and the rule of law. Such leadership can reverse the downward spiral of impoverishment, hunger, and disease experienced by certain parts of the world, ultimately ending the significant suffering of the poor.
Further, the government should take on well-designed credit programs to stimulate economic growth and enable poor communities to access financial capital for investment in income-generating activities. In this vein, inclusive economic growth must be adopted to enable impoverished communities to utilise their resources to increase both their output and incomes and thus break the poverty trap and be able to provide for their basic needs.
achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and how they link to eradicating global poverty
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a global plan for countries to work together to improve the well-being of people, protect the planet, and promote prosperity. This comprehensive framework recognises the intricate connections between different dimensions of development and poverty eradication. Achieving these goals, especially SDG 1 (to “end poverty in all its forms everywhere”), lays the foundation for addressing the root causes and consequences of poverty, leading to a more equitable and sustainable world.
A Thrivable Framework
The THRIVE Framework examines issues and evaluates potential solutions in relation to this overarching goal of thrivability. It is about making predictive analyses using modern technology that supports environmental and social sustainability transformations.
Sustainable technology can mitigate global poverty, hunger, and climate change. Eradicating global poverty will require a greater commitment to reducing inequality within and between nations, which will likely necessitate higher growth rates in the poorest nations. Moreover, in an inclusive society, it is not enough to simply get everyone above an absolute minimum standard of living. Economic growth must increase the prosperity of poor people over time.
To learn more about how THRIVE Project is researching, educating, and advocating for a future beyond sustainability, please visit our website. You can follow our informative blog and podcast series to learn about our regular live webinars. We feature experts in sustainability fields, including many rich discussions on social inclusion. Sign up for our newsletter for regular updates.