Water pollution is the contamination of water sources by substances that make the water unusable for daily usage. Pollutants include chemicals, trash, bacteria, and parasites. All forms of pollution eventually make it unattainable.
Water pollution leads to water shortage
Water is one of the essential compounds for all living beings. Even though 71% of Earth’s surface is water, only 0.5 per cent of Earth’s water is available as a fresh water resource.
Water pollution is a major problem that the world has been facing since the dawn of civilisation. And human beings are responsible for that act. Contaminated water is unusable for daily chores, such as cooking, washing, and bathing. In addition, hard or contaminated water is not suitable for commercial use. This is due to the presence of pollutants such as chemicals, bacteria, and parasites.
Water shortage is a persistent global issue. Countries in many parts of the world are water-stressed. And they’re trying hard to overcome their baseline water stress problem.

Source: World Resources Institute
Causes of water pollution
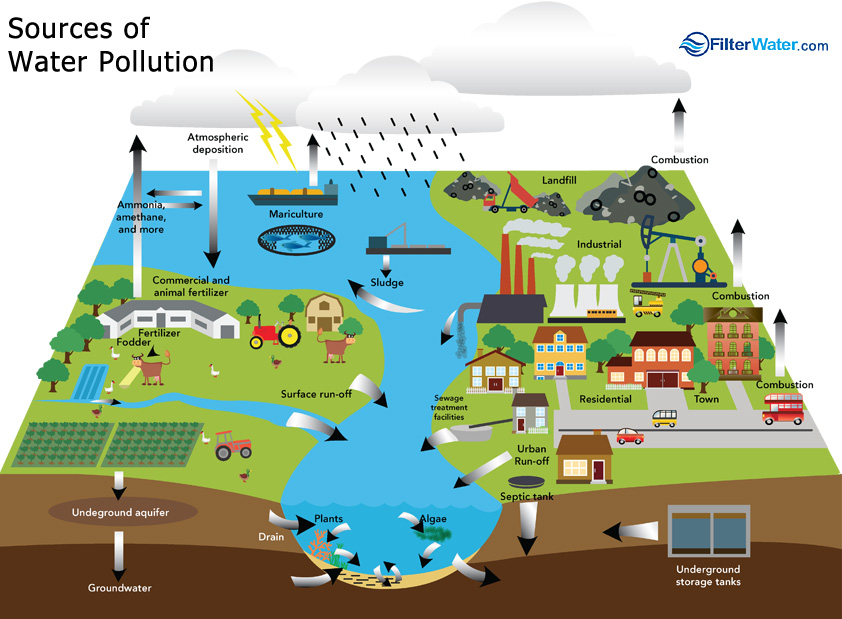
Water pollution occurs when water bodies are contaminated by toxic substances, often chemicals and microorganisms. Factors contributing to contamination include dumping of industrial waste, temperature rise, and deforestation. Consequently, water pollution causes many negative effects on humans and the environment. It damages biodiversity when harmful algae form in contaminated water. And poses a danger to human health.
There are numerous causes contributing to water pollution. Six are mentioned below:
1. Rapid urbanisation
Urban population growth spurs developments in housing, infrastructure, and industries. And increased urban activities produce more household, chemical, and industrial waste. These pollutants find their way into rivers and streams with rainwater. Thus, contaminating water bodies.
2. Improper sewage disposal
Improper sewage disposal is a major issue in many countries. Particularly in low-income nations where sewage treatment plants are non-existent. As a matter of fact, more than 80% of global sewage flows into our seas and oceans untreated. Untreated wastewater contains substances that are harmful to marine plants and animals. And contaminates the seafood that we eventually consume.
3. Fertiliser run-off
It’s common practice for farmers to use fertilisers to boost crop yields. Excess fertilisers not absorbed by plants seep into the soil. And from there, they run off into waterways by way of groundwater, or rainwater.
4. Oil spills
Oil spills most often happen because of accidents involving oil tankers, pipelines, refineries, and drilling rigs. In addition, spills can also occur due to human error, equipment breakdown, and natural disasters. Oil spills contaminate large parts of the ocean. It then seeps into freshwater bodies that are connected to the ocean.
5. Chemical waste disposal
Though illegal, the act of dumping chemical and industrial waste into water bodies continues. The most toxic waste material dumped into the ocean includes dredged material, industrial waste, sewage sludge, and radioactive waste. Marine animals suffer toxic effects. And marine plants that are sensitive to pollution, like seagrass, die. The loss of biodiversity has a ripple effect on marine life. One habitat is usually food or a life source for another. And when that habitat dies, dependent habitats find it hard to survive too.
6. Radioactive waste disposal
Water is essential for cooling reactors in nuclear plants. During the cooling process, the water gets contaminated with radionuclides. It then undergoes a filtering process to remove as much of the radionuclides as possible. Subsequently, it’s released into the ocean when deemed to have “safe” levels of radioactive materials. But, disasters do happen. Like, in the case of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant. It was damaged by an earthquake and tsunami in 2011. In the days following the event, tonnes of radioactive materials escaped into the atmosphere and the Pacific Ocean.
Effects of water pollution
Impact on human health
Water pollution harms human health in many ways, directly and indirectly. By definition, polluted water is water that’s contaminated with harmful substances. To the extent that it’s no longer usable. Hence, it can’t be used for drinking, or for essential industries like agriculture.
Every year, more than 500,000 people globally die from diseases related to the consumption of polluted water. For example, diarrhoea, cholera, dysentery, typhoid, and poliomyelitis.
In addition, consuming contaminated water can lead to the development of long-term health issues. They include gastrointestinal illness, reproductive problems, and neurological disorders. Infants, young children, pregnant women, senior citizens, and people with compromised immune systems are at a higher risk of developing these problems.
The availability and adequacy of clean water are also major concerns in many countries. Particularly in low-income countries where quality healthcare is still lacking. Globally, 15% of patients develop an infection in health care facilities that lack clean water for their operational use.
Impact on the Environment
There is a huge impact on the environment too. For instance, the use of fertilisers in agriculture, and their run-off to rivers and lakes. Nutrients in the fertilisers promote the growth of microorganisms and harmful algae on the surface of the water. They deplete oxygen and prevent sunlight from penetrating the water. Thus, choking marine life.
Oil spills on the Baltic Sea are another good example. A case study on the second-largest oil spillage in the Baltic Sea revealed devastating effects on the marine environment. It found seawater, sediments, and marine life contaminated with PAH (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons). What’s more, many birds of 23 different species were found dead or dying in the area. These birds had oil-smeared feathers, and damaged respiratory and ingestion organs.
The Ganga River in India is yet another example. It’s heavily polluted with microplastics. In fact, more than any other major river in the world. Microplastics are not only toxic, they can absorb toxins from other sources in the water as well. Moreover, they may also carry disease-causing organisms on their surface. When contaminated water is used in irrigation, it harms the organisms that maintain the fertility of the land.
Solutions to water pollution
There are many methods to control water pollution. Some of them are:
For individuals
- Consume more organic food. This reduces the demand for crops grown with industrial fertilisers.
- Avoid the use of harmful chemicals for cleaning. Switch to natural cleaners such as lemon and vinegar instead.
- Practice water conservation. For example, harvest rainwater for use in daily chores.
- Dispose of household chemicals responsibly.
For governments and businesses
- Plant more trees to control erosion and stormwater pollution.
- Encourage the use of recyclable materials.
- Protect water sources and monitor their utilisation levels.
- Dispose of industrial and chemical waste safely.
- Promote ecotourism, and prohibit the use of plastic bags near beaches and water streams.
- Invest in wastewater treatment plants to recycle water for industrial purposes.
It’s everyone’s responsibility to conserve water. And the habit is best cultivated from a young. Whether at home or in school, it’s important to educate children on conservation methods. This will encourage them to be responsible environmental citizens of the future.
And for governments, enforcing conservation policies, and investing in innovations are vital. Particularly in the areas of wastewater and landfill management. They are necessary to safeguard our water bodies from further degradation. In addition, governments should encourage businesses to invest in eco-friendly or organic products. They can do this by providing incentives and tax benefits. Finally, they should encourage citizens to practice water conservation in their media campaigns.
Thrivability matters
At THRIVE, we believe in every action that protects water resources. This includes the efficient management and distribution of water. We need to take action as our well-being depends on it. We need to look at our own responsible consumption and know what other measures we can take.
Your actions are important. For more information on how THRIVE can support your actions, please visit our webpage. If you want to know more about sustainability issues, read our blog.