Harnessing human waste for energy is one solution being proposed to help meet future energy demand.
Each year, the United States generates more than 70 million tonnes of organic trash. Poor waste management poses many risks to human health. That includes the infection of subsurface fresh drinking water and increases in the ratio of nitrates contained in it.
However, biogas and biomass technology in waste management promise economical sources of power that will help to reduce organic trash and combat greenhouse gas emissions.
What Is The Main Difference In Biogas And Biomass?
When organic waste decomposes it releases methane gas, which is a powerful green house gas that traps heat in the atmosphere.
Biogas, more specifically, is a product of Anaerobic digestion. Biogas generates energy using decomposing food waste in the absence of oxygen.
Biomass, on the other hand, is generally sourced from crop waste, wood, and other combustible materials. Biomass energy is produced through the burning of these resources in the presence of oxygen.
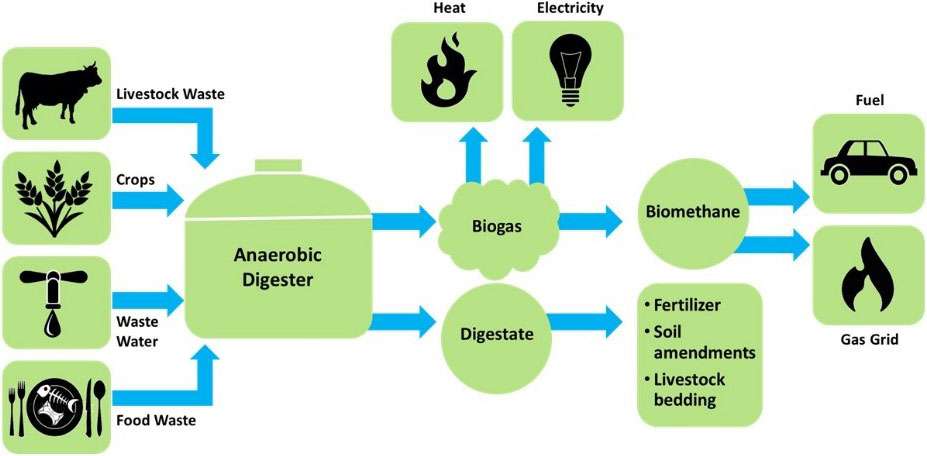
How Are Biogas and Biomass sustainable?
In the United States 80% of natural gas is recovered by fracturing. This is the process of pumping a fluid, typically a mix of water, sand and chemicals, into a wellbore at very high pressures. Fracturing breaks apart rock formations in order to release gas reserves.
However, in recent years, biogas has emerged as a “greener” fuel alternative. It is much more sustainable and cost-effective compared to subsurface natural gas.
Biogas energy is also easier to use in electricity production, ground transportation, and commercial and residential buildings.
Meanwhile, we can generate power from zero-carbon sources. The best examples are wind and solar. Countries like the USA, Australia, Canada, and China are upgrading their energy processing techniques to renewable energy.

In 2020, Canada produced 6 million gigajoules (6 GJ) of energy through RNG, 260 million m3 of biogas for heat, direct use and fuel to provide 196 megawatts of clean electricity capacity.
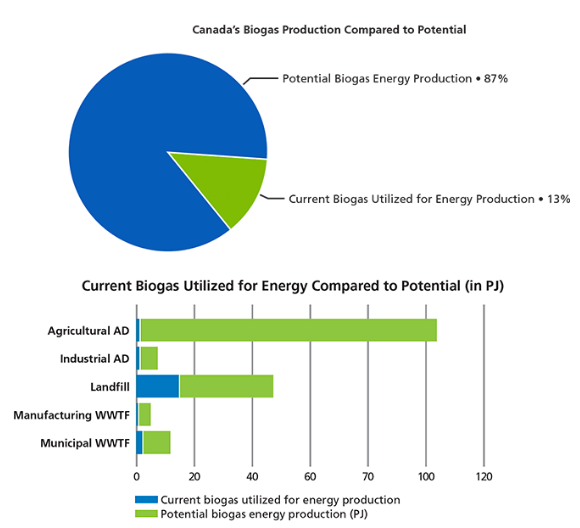
According to the Canadian 2020 Biogas Market Report, Canada is only using 13 % of its easily accessible biogas potential. Which means that biogas output could grow eight times more.
Why Is waste for energy useful in Pakistan & India?
Pakistan has struggled with problems of energy deficiency in the last decade. Every year, the Pakistani government spends more than 14.5 billion US dollars to import crude oil to fill the energy gap.
Furthermore, Energy demand is increasing rapidly but exploration and use of renewable energy have not met the need. On average, power outages in Pakistan last for about 14 – 20 hours per day.
Pakistan has an annual livestock growth rate of 4% and livestock is the source of dung waste. It can produce 35.625 million kWh of electric energy per day. Efficiently using biogas as an alternative energy source will help in overcoming the challenge.
Besides the cost-saving benefit of installing a biogas plant, health-wise, it is also beneficial in reducing respiratory and eye infections. PCRET has installed 4109 biogas plants across the country, saving an average of Rs. 37.925 million per month.
India started a biogas promotion program between 1981-82 and plays a leading role in the development and dissemination of renewable energy technology. Biomass remains the primary source of energy for cooking in rural India, accounting for approximately 75% of total energy consumption.
It has the potential to generate 6.38×1088 m3 of biogas and 350 million tonnes of manure from the 980 million tons of dung that are available annually.
Conclusion
Although biogas is a more sustainable solution than traditional natural gas today, we should consider it as an important transition fuel on the road to completely decarbonizing our energy supply.
Human waste is a reliable and economical source of renewable energy when properly harnessed. Many major industries like fertilizer, oil, and gas are also changing their theme to focus on carbon net-zero.
The natural subsurface energy resources contribute to atmospheric pollution and disease. Countries like the USA, Australia, Canada, and China are upgrading their energy processing techniques to renewable energy, replacing natural gas with biogas.
Due to energy crises, Pakistan and India have turned their focus on biogas energy which is more economical and easily accessible to their people as they have two of the densest South Asian populations.
In order to achieve proper balance of our global energy mix, we must embrace biogas and continue to seek ways to get more value from organic waste.
Connect with the THRIVE Project to gain more knowledge on affordable, sustainable, and clean energy for all. Subscribe to our newsletter here.